When travelling to Laos, understanding the basics of the local language can greatly enhance your experience and interactions. Familiarising yourself with common phrases and cultural Laos language practices will not only help you navigate through daily activities more smoothly but also show respect to the locals, who appreciate visitors making an effort to speak their language. This guide provides essential Laos language basics tailored for travellers, helping you connect more deeply with the people and culture of this beautiful country.
I. The official language of Laos
1. Lao - official language in Laos
The Lao language, also known as Laotian, is the official language of Laos, it is used by majority of the national population, which clearly makes it the most popular language in the country. Additionally, around 15 million people in Thailand's Isan region, also known as the northeast, speak Lao, where it is referred to as the Isan language. Beyond Southeast Asia, there are significant Lao-speaking communities in the United States, with smaller populations in Canada, Cambodia, and the United Kingdom.
Laos country language belongs to the Tai language group, which is part of the Kra-Dai language family (a tonal language of the Tai-Kadai family). This family also includes Thai, Shan, and various languages spoken by smaller ethnic groups across Laos, Thailand, Burma, southern China, and northern Vietnam. Languages in the Tai family share similar grammatical and tonal structures.
The language of Laos and Thai are quite similar, which means many Laotians can understand spoken Thai, and literate individuals can read it as well. In Thailand's northeastern region, Lao is known as Isan and is spoken by the Isan people, who have the same ethnic background as the Lao.
Lao features a tonal system with six tones in the
Vientiane dialect: low, mid, high, rising, high falling, and low falling. The meaning of a word can change based on its tone, so clear pronunciation is crucial to avoid misunderstandings.
Lao is a concise language. Prefixes and combinations of basic words are used to make more complex meanings. The sentence structure is also quite simple and "grammar" refers mostly to word order.
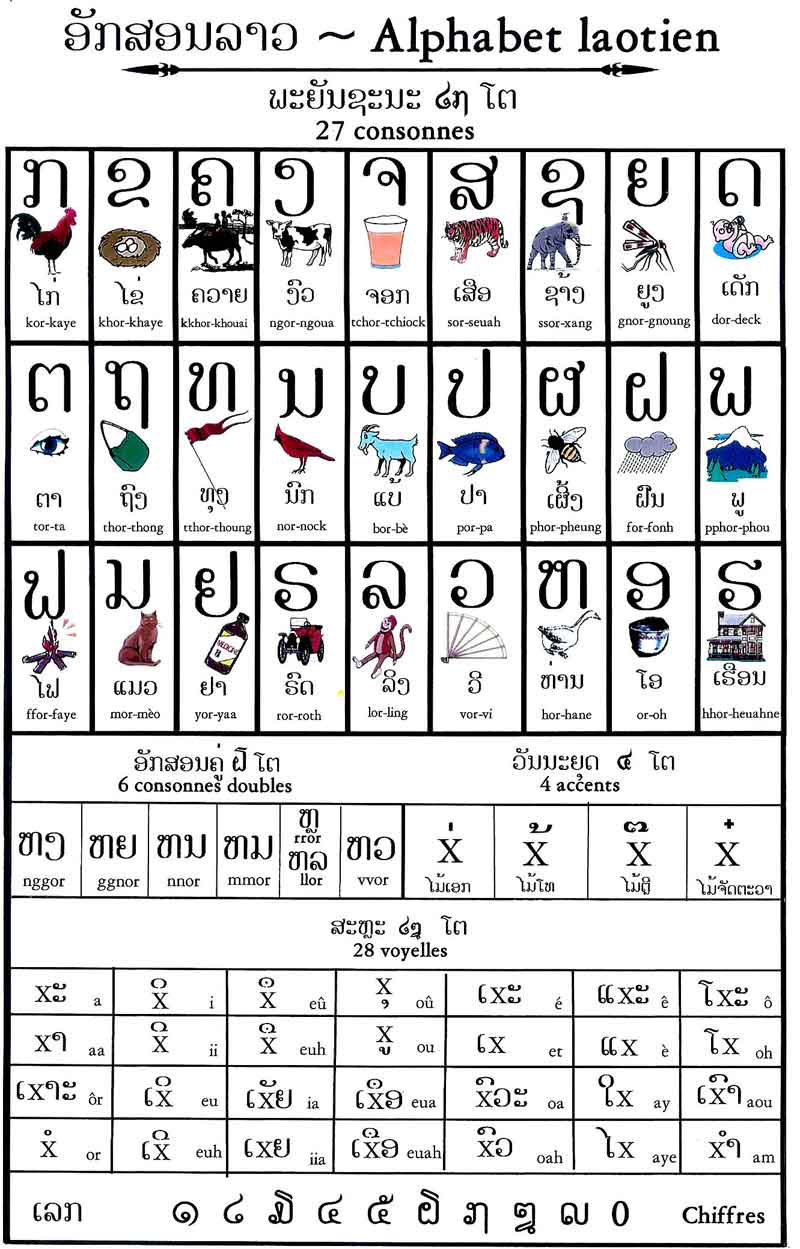
The script used to write Lao language has the same Brahmic base as Thai and Khmer, (though it is not intelligible with Khmer) and Thai readers will be able to figure out most of it. The Lao writing system evolved from Sanskrit. It was first taken by the Khmers during the time of the Angkor Empire then adapted by the Laotians, Northern Thais, and Central Thais into individual though similar alphabets. This Laos language alphabet is composed of letters with their own sounds and are read from left to right like English. The Lao script comprises 28 vowel sounds and is derived from 27 consonant symbols and 18 vowel symbols.
The majority of Lao vocabulary is composed of just one syllable. Words with many syllables are typically employed at a higher level in academia, government, and religion.There are no spaces between words; instead spaces in a Lao text indicate the end of a clause or sentence.
There is no official Latin transliteration system for the language of Laos. In Laos, French-based systems are used and there is considerable variation in spelling, particularly of vowels.
2. How to say some simple sentences in Laos language?
When travelling to Laos, one of the first things people often want to know is how to say hello in lao. Before diving into Lao sentences, it's crucial to remember a key greeting for your trip to Laos: "Nop". This gesture is a sign of respect and is used to show deference to people and things alike. It’s commonly performed when passing by sacred sites like temples or other religious locations, demonstrating your reverence and politeness.
For men greeting other men, when they want to say hello in laos language, it is generally customary to clasp hands and slightly bow or nod.
For women greeting other women or men greeting women, it is common to press hands together just below the chin, accompanied by a slight bow
Here are some simple sentences in the
language of laos along with their
laos language to english translations to help you get started:
English | Lao |
| Hello! | Sabaidee! (ສະບາຍດີ!) |
| How are you? | Sabaidee baw? (ສະບາຍດີ ບໍ່?) |
| I’m fine, thank you. | Koy sabaidee, khop chai. (ຂໍໍາສະບາຍດີ, ຂອບໃຈ.) |
| What is your name? | Jao seu aei? (ເຈົ້າ ຊື່ ແມ່ນແບບໃດ?) |
| My name is [Your Name] | Koy seu [Your Name]. (ຂໍໍາຊື່ [Your Name].) |
| I don’t understand | Koy baw khao jai. (ຂໍໍາບໍ່ ເຂົ້າໃຈ.) |
| Can you help me? | Jao hil koi dai baw? (ເຈົ້າ ຮິບ ເຂອງແດ່ບໍ່?) |
| How much is this? | Nèe tao dai? (ນີ້ ເທົ່າໃດ?) |
| Goodbye! | La khãwn (ລາກ່ອນ) |
| Yes No | Jao (ແມ່ນແລ້ວ) Baw (ບໍ່) |
In addition, you can also learn the following short, easy-to-remember sentences, which enhance your experience in trip to Laos
English | Lao |
| What is this? | An nee maen yang? |
| How much is it? | Laka tao dai? |
| It’s too expensive! | Peng phot |
| It’s very cheap | Bo peng |
| I want to buy… this one! | Khaphachao…yakcha su... thini |
English | Lao |
| Can you help me | Suay khoy dai boh |
| Where is…? | Bonthi pen...? |
| How to go to…? | Vithikan pai...? |
| Excuse me, could you tell me how to get to ….. ? | Khoothd chao bok khony daibo va paihodsai …? |
| Is it a long way? | Manpen thang nyav |
| How far is it? | Man kai theoadai |
II. Other language of Laos of minority
1.Kmur
The Khmu language, spoken by the Khmu ethnic group in Laos, is an integral part of the country’s rich linguistic tapestry. As a member of the Austroasiatic language family, Khmu is predominantly used in the northern regions of Laos, including areas like Luang Prabang and Phongsaly. With its own distinct phonetic and grammatical structure, Khmu features a variety of dialects that reflect the diverse cultural heritage of its speakers. This Laos language is characterised by its use of a complex system of tones and a unique set of vowel sounds, distinguishing it from other local languages of Laos. Khmu serves not only as a means of daily communication but also as a key component of the cultural identity and traditional practices of the Khmu people.
2. Hmong
The Hmong language, spoken by the Hmong ethnic group in Laos, is a vibrant and distinctive language within the larger Hmong-Mien language family. Predominantly used in the mountainous regions of northern Laos, such as in the provinces of Xieng Khouang and Luang Namtha, Hmong is known for its rich oral tradition and complex tonal system, which includes up to eight different tones depending on the dialect. The Laos country language features a unique set of phonetic sounds and is written using both traditional Hmong script and the Latin alphabet. Hmong serves as a crucial medium for preserving cultural heritage and transmitting traditional knowledge, making it an essential element of the Hmong people's identity and community life in Laos.
III. Foreign language spoken in Laos
1. English
English in Laos, while not a native language, plays a growing role, particularly in urban areas and among younger generations. Often used as a second Laos language in business, tourism, and education, English is increasingly taught in schools and universities across the country. It serves as a key tool for international communication and economic development, reflecting Laos' expanding global connections. In tourist hotspots and among expatriate communities, English is commonly spoken, making it a valuable asset for travellers and professionals navigating the local landscape. Despite its rising prominence, Lao remains the dominant language for everyday communication and cultural expression in Laos
2. French
French, a remnant of Laos' colonial past, is still spoken by a segment of the population, particularly in academic, governmental, and diplomatic circles. During the French colonial period, which lasted from the late 19th century until the mid-20th century, French influence shaped many aspects of Laotian society, leaving a lasting legacy in the form of the French language. Today, French is often used in higher education and in international relations, and it is taught in some schools and universities. While its usage is less widespread compared to Laos country language or English, French remains a valuable language for those engaged in cultural exchange and historical studies, reflecting Laos' rich historical ties with France.

The Laos language is a key cultural pillar, uniting diverse ethnic groups in Laos and preserving the nation’s rich history and identity. As the official language of Laos, it fosters national unity and pride, essential for maintaining cultural heritage and supporting Laos’s development. In a globalised world, safeguarding Lao ensures the country's unique identity is retained and its voice is heard internationally.
AUTOUR ASIA - Asia Travel Agency trust that the details in this article will enhance your journey, making your travel experience in Laos truly unforgettable.
Are there any common gestures or body language cues I should know when speaking Lao?
Yes, when in Laos, it’s polite to use both hands when giving or receiving something, as a sign of respect. Avoid touching someone’s head, as the head is considered sacred, and refrain from pointing your feet at others, since feet are viewed as the lowest part of the body. Approach interactions with calmness and humility, as these qualities are highly valued in Lao culture.
Are there any cultural aspects tied to language of Laos that tourists should be aware of?
Yes, in Laos language, using gestures is essential. Greet with "Sabaidee" and a slight bow or nop (hands pressed together). Adding "khab" for men or "ka" for women at the end of sentences shows respect, especially to elders or those of higher status. Lao culture values calm, modest communication, so speaking softly and avoiding confrontation is important. Understanding these cultural nuances will help you interact respectfully and positively in Laos.