Thailand, with its dreamy beaches, fascinating culture, and exquisite cuisine, attracts millions of visitors each year. However, to fully enjoy this enchanting country, it is crucial to understand its monetary system. What is the currency in Thailand? This article provides you with all the necessary information to master the monetary system in Thailand. You will discover how to efficiently manage your money during your stay. Whether you are a seasoned traveler or new to Southeast Asia, our advice will help you avoid financial inconveniences and make the most of your vacation. Before packing your bags, consult our comprehensive guide on currency in Thailand.
I. Introduction to the currency in Thailand
When traveling to Thailand, understanding the local currency is essential for a smooth and enjoyable experience. What is the currency in Thailand? The official currency of Thailand is the Thai Baht (THB), and familiarizing yourself with its usage will help you navigate financial transactions during your stay.
When dealing with currency exchange or financial transactions in Thailand, you'll often see the currency referred to by its ISO code, THB. This code is universally recognized in international banking and foreign exchange markets. In more casual or local contexts, you might hear the currency simply called "baht" Thai Baht or see prices written with the ฿ symbol.
II. Basic information about the currency in Thailand
1. Thai baht exchange rate
As updated in August 2024, the Thai baht exchange rate is approximately 1 euro for 39 baht and 1 USD for 37 baht. However, it's crucial to remember that exchange rates fluctuate regularly. It is highly recommended to check the current rate before your departure for Thailand to ensure you have the most up-to-date information for your trip.
2. Denominations
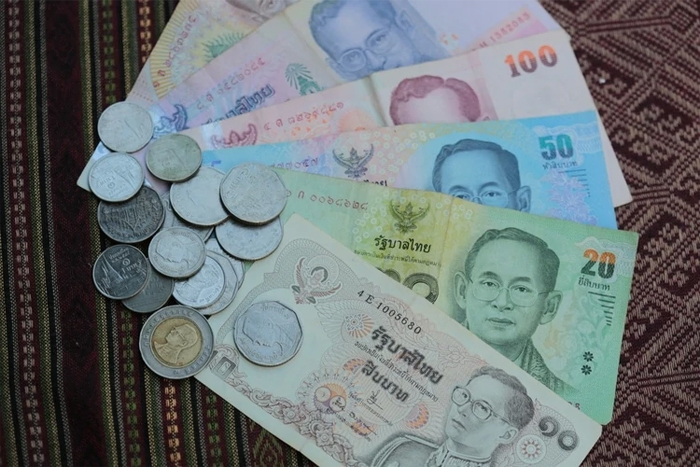
The currency in Thailand comes in both banknotes and coins, each with distinct denominations.
a. Banknotes
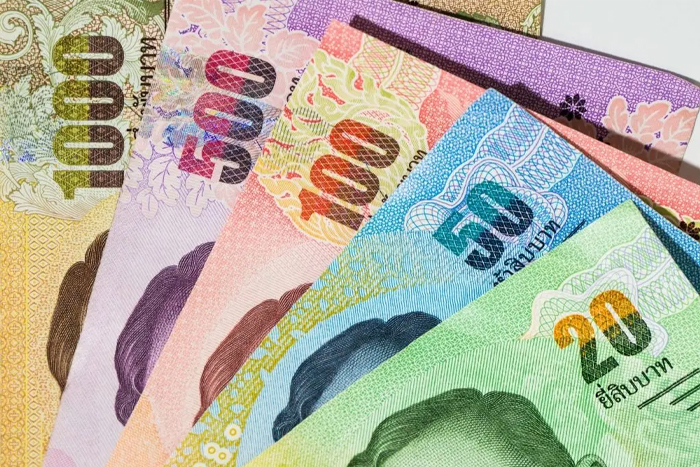
Banknotes in Thailand are colorful and vary in size, making them easily distinguishable. They are available in denominations of 20, 50, 100, 500, and 1000 baht. The 20-baht note is the smallest and is green in color, while the 1000-baht note is the largest and features a purple hue. Each banknote depicts the image of the Thai king on one side and various important Thai landmarks or historical figures on the other.
b. Coins
Coins in Thailand are equally diverse. They come in denominations of 1, 2, 5, and 10 baht. Additionally, there are smaller denominations called satang, with 100 satang equal to 1 baht. You might encounter 25 and 50 satang coins, although these are increasingly rare in everyday transactions. The 10-baht coin is bi-metallic, with a copper-colored center and a silver-colored ring, making it easily identifiable.
III. How to get Thailand baht?
How to get Thailand baht? When preparing for your trip to Thailand, obtaining Thai Baht is a crucial step. There are several methods to acquire the currency in Thailand, each with its own pros and cons. Understanding these options will help you make the best choice for your needs and potentially save money on exchange rates and fees.
1. Currency exchange
Currency exchange is a common option. You can exchange money at home before travel, which provides the security of having local currency upon arrival. However, the Thai baht exchange rate is often less favorable than those in Thailand. Once in Thailand, banks typically offer the best exchange rate for thai baht but may have limited hours. Exchange booths in tourist areas provide convenience and extended hours, but rates vary, so compare before exchanging. Be cautious of suspiciously good rates, as they may be scams. Hotels also offer currency exchange, which is convenient for off-hours needs, but their rates are usually less favorable. Use hotel exchanges sparingly, mainly for small amounts or emergencies. As a best practice, always count your money after exchange and keep your receipts.
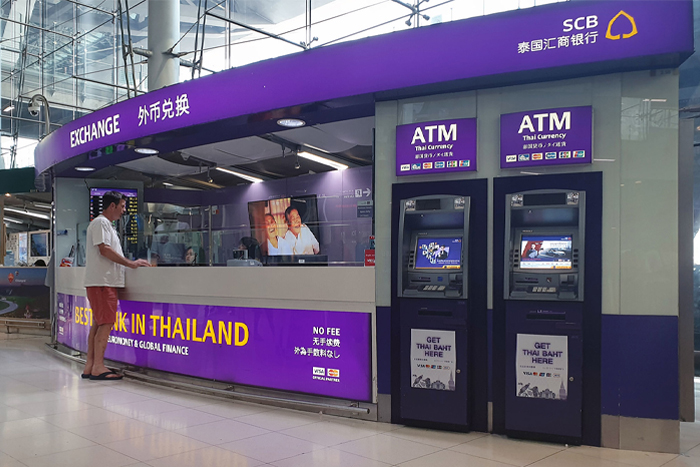
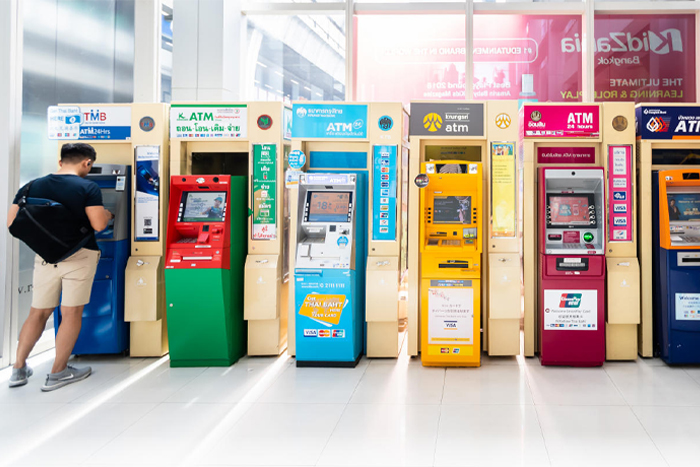
2. ATM usage
How to get Thailand baht? ATM usage is another popular method for obtaining Thai Baht. ATMs are widely available in cities and tourist areas, offering 24/7 access to local currency. However, be aware of fees and limits. Your home bank may charge foreign transaction fees, and Thai banks often impose a fee for international card usage (around 220 baht per transaction as of 2024). Daily withdrawal limits also apply, so check with your bank beforehand. For safety, use ATMs inside banks or in well-lit, secure locations, and be aware of your surroundings.
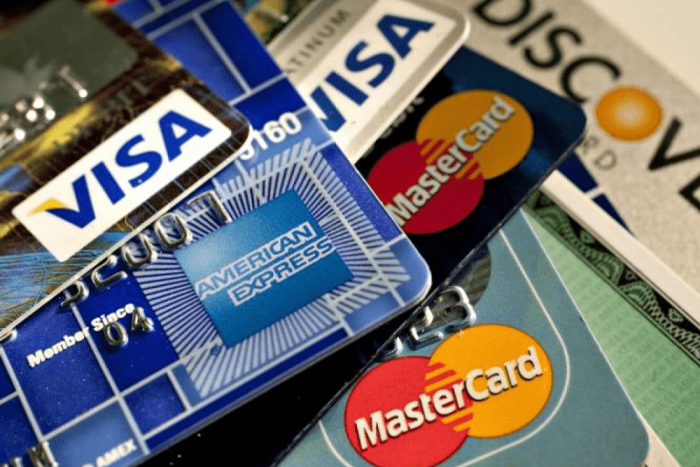
3. Credit and debit card use
International credit cards and debit cards are widely accepted in Thailand's urban and tourist areas, especially at hotels, restaurants, and larger shops. However, cash is preferred for smaller purchases and in rural areas. Be aware of potential foreign transaction fees. Some international credit cards offer fee-free foreign transactions, which can save you money. Always check with your card issuer about fees before traveling to have the best exchange rate for thai baht.
IV. How to pay during your stay in Thailand
During your stay in Thailand, you'll have several payment options at your disposal. Cash remains the most widely accepted method, especially for small purchases and in rural areas. However, international credit and debit cards are increasingly popular in urban centers and tourist spots, particularly at hotels, restaurants, and larger shops.
Budgeting for your trip can vary widely depending on your travel style. Thailand can be quite affordable, especially if you're willing to embrace local experiences. Costs differ significantly between budget accommodations and luxury resorts, street food and high-end restaurants. Transportation expenses also range from affordable public buses to pricier taxis or rental cars.
Some useful travel tips
Always carry some cash, especially when visiting markets or street vendors.
Be cautious of counterfeit bills. Familiarize yourself with genuine banknotes.
Exchange money at banks or official exchange booths for better rates. Avoid exchanging at airports if possible.
Small denominations are useful for taxis, street food, and markets.
Tipping is not mandatory but appreciated for good service.
Some tourist areas may accept US dollars, but using baht is generally better.
Check exchange rates before your trip and consider using a currency conversion app.
In conclusion, managing your money in Thailand involves understanding the
currency in Thailand, knowing your options for obtaining and using it, budgeting appropriately, and staying safe. By keeping these factors in mind, you'll be well-prepared to handle financial matters during your Thai adventure, leaving you free to enjoy the country's rich culture, stunning landscapes, and renowned hospitality.
We hope the information about
currency in Thailand is helpful and assists you in having an enjoyable and authentic experience in Thailand. We believe you will have a wonderful journey and many memorable experiences. For a satisfying experience that exceeds your expectations, please CONTACT ATOUR ASIA,
Thailand Travel Agency now.